INTRODUCTION
What is Automation ?
Overview of Automation
Motivation
Automation in industry
Examples from different industry sectors
What is automation ?
Benefit of automation is that it saves labor; however,
it is also used to save energy and
materials and to improve quality, accuracy and precision.
Automation is basically the delegation of human control function to technical equipment for
Automation is basically the delegation of human control function to technical equipment for
1. Increasing productivity
2. Increasing robustness (consistency)
3. Reducing direct human labor costs and
expenses.
4. Increasing
quality
History of automation
Manual Control
Pneumatic Control
Hard wired logic
Control
Electronic
Control using Logic Gates
Programmable
Logic Controller
1. Manual Control
All
the actions related to process control are taken by the operators manually.
Disadvantage
Likely human errors and consequently its effect on
quality of final product.
The production, safety, energy consumption and usage of raw material are all subject to the correctness and accuracy of human action.
The production, safety, energy consumption and usage of raw material are all subject to the correctness and accuracy of human action.
2. Pneumatic Control
Industrial automation, with its machine and process
control, had its origin in the 1920s with the advent of "Pneumatic
Controllers“.
Actions were
controlled by a simple manipulation of pneumatic valves, which in turn were
controlled by relays and switches.
Disadvantage
Bulky and Complex
System
Involves lot of
rework to implement control logic
Longer project
time
3. Hard wired logic Control
The contactor and relays together with hardware timers and counters were used in achieving the desired level of automation
Disadvantage
Bulky panels
Complex wiring
Longer project time
Difficult maintenance and troubleshooting
Difficult maintenance and troubleshooting
4. Electronic Control using Logic Gates
In 1960s with the advent of electronics, the logic gates started replacing the relays and
auxiliary contactors in the control circuits.
auxiliary contactors in the control circuits.
The hardware timers & counters were replaced by
electronic timers.
Advantage
Disadvantage
Reduced space requirements
Energy saving
Less maintenance & greater reliability
Less maintenance & greater reliability
Disadvantage
Changes in control logic not possible
More project time
More project time
5. Programmable Logic Controller
In 1970s with the
coming of microprocessors and associated peripheral chips, the whole process of
control and automation underwent a
radical change.
Instead of
achieving the desired control or automation through physical wiring of control
devices, in PLC it is achieved through a
program or say software.
The programmable
controllers have in recent years experienced an unprecedented growth as
universal element in Industrial Automation.
It can be effectively used in applications ranging from simple control like replacing small number of relays to complex automation problems.
It can be effectively used in applications ranging from simple control like replacing small number of relays to complex automation problems.
Advantages of PLCs
Reduced space
Energy saving
Ease of
maintenance
Economical
Greater life
& reliability
Tremendous
flexibility
Shorter project
time
Easier storage,
archiving and documentation
Industrial automation main components
Field instrumentsControl hardware
Control software
Automation : Typical installation...
Automation : Typical installation...
Sensors or Transducers (Field Instruments)
Sensors are used to sense the changes in physical
parameter like Temperature, Level, Flow, Humidity, Pressure and many others..
Transducers are
used to convert not electrical quantity to electrical signals
Hence it
concludes, sensors and transducers are placed in field to sense the physical
parameters and send the electrical signal of respective changes to control
rooms.
These signal are
either digital or analog signals for example, Ohm(RTD), mv(Thermocouple), standard 4-20mA signal, etc.
Widely used field instruments in industries
Flow transmitters
(Orifice, Ventury, Electromagnetic flow meter etc)
Pressure
transmitters (Bourdon gauge, Bellows, Diaphragm, etc)
Temperature
transmitters (Thermocouple, RTD, Thermister, etc)
Level Transmitter
(Ultrasonic transmitter, Radar type, capacitive type)
pH transmitter
Conductivity
Meter...etc
Famous manufacturing companies (Field instruments)
Fisher Rosemount
Yokogawa
Endress+Hauser
Forbes Marshall
Honeywell ABB
Yokogawa
Endress+Hauser
Forbes Marshall
Honeywell ABB
Control hardware
Standalone PID
Controllers
Programmable logic controllers
Distributed control system
Programmable logic controllers
Distributed control system
1. Standalone PID Controllers
This can be installed in field or in control room
Every companies have variations in programming patterns to setup PID configuration
Typical installation of standalone PID controller
Famous manufacturing companies in PID controllers
ABB
Yokogawa
Moore
Forbes Marshall
Honeywell
Eurotherm
ASCON
Yokogawa
Moore
Forbes Marshall
Honeywell
Eurotherm
ASCON
2. Programmable logic controllers
A programmable logic
controller (PLC), or programmable controller is an industrial
digital computer which has been ruggedized and adapted for the control of
manufacturing processes, such as assembly lines, or robotic devices, or any activity that
requires high reliability control and ease of programming and process fault
diagnosis.
What is inside PLC ?
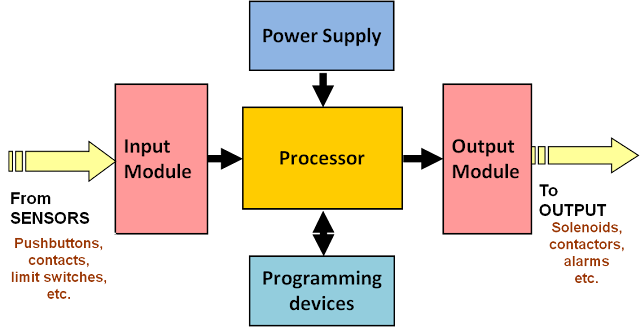 |
| Architecture of PLC |
A programmable logic controller (PLC), is a like a microcontroller which is used for doing so many applications.
It basically
consist of
1. CPU with
processor and program memory
2. Power supply
3. Input module
4. Output module
5. Control bus
1. Parts of Delta PLC
2. Parts of Allen Bradley PLC
3. Parts of Siemens PLC

4. Parts of Zelio Schneider electric PLC
Distribution of I/O's through controller
Distributed control system (DCS)
 |
| General architecture of DCS |
System cabinets and Marshalling cabinets of DCS
 |
| System and Marshalling cabinet arrangement |
Various DCS and Hybrid DCS providing companies
DCS
1. Yokogawa (Centum VP)
2. Honeywell (EPKS)
3. Emerson (Delta V)
4. Forbes Marshall
Hybrid DCS
1. Allen Bradley (Compact logix and control logix)
Various Communication protocol used in DCS or PLC systems and its hierarchy
LAN (Ethernet)
Modbus, CAN,
Serial communication
OPC (OLE for
Process Control)
Control NET
Foundation Field
bus
Profibus (DP,PA)
Device NET
Various languages used in PLC and DCS
Ladder Logic ( LAD/LD)
Function Block
Diagram (FBD)
Sequential
Function Chart (SFC)
Structured Text
(ST)
Instruction List
(IL )
Supervisory Control and Data Acquisition software (SCADA)
SCADA (supervisory control and data acquisition) is a category of
software application program for process control, the gathering of data in real
time from remote locations in order to control equipment and conditions.
Features of typical SCADA software
Dynamic process graphic
Real-time and Historical trending
Alarms
Recipe Management
Security
Device connectivity
Script for logic development
Database connectivity
Displays used for monitoring in SCADA systems
Some SCADA software available in market
Intouch (Wonderware factory suit)
Wincc (Siemens)
Simplicity (GE Fanuc)
Core
branches/career of Instrumentation and its scope in Industry
JOB OPTIONS
EPC
Engineering
Procurement and construction
Designing of
total plant
Automation work
includes in EPC companies
Designing of
P&ID drawings
Automation
Designing of the
Automation system
Erection and
Commissioning
Maintenance and
Troubleshooting of existing system












